The liver plays a crucial role in processing these nutrients and removing toxins from the bloodstream. It also stores glycogen, which is a form of glucose that provides energy to the body when needed.
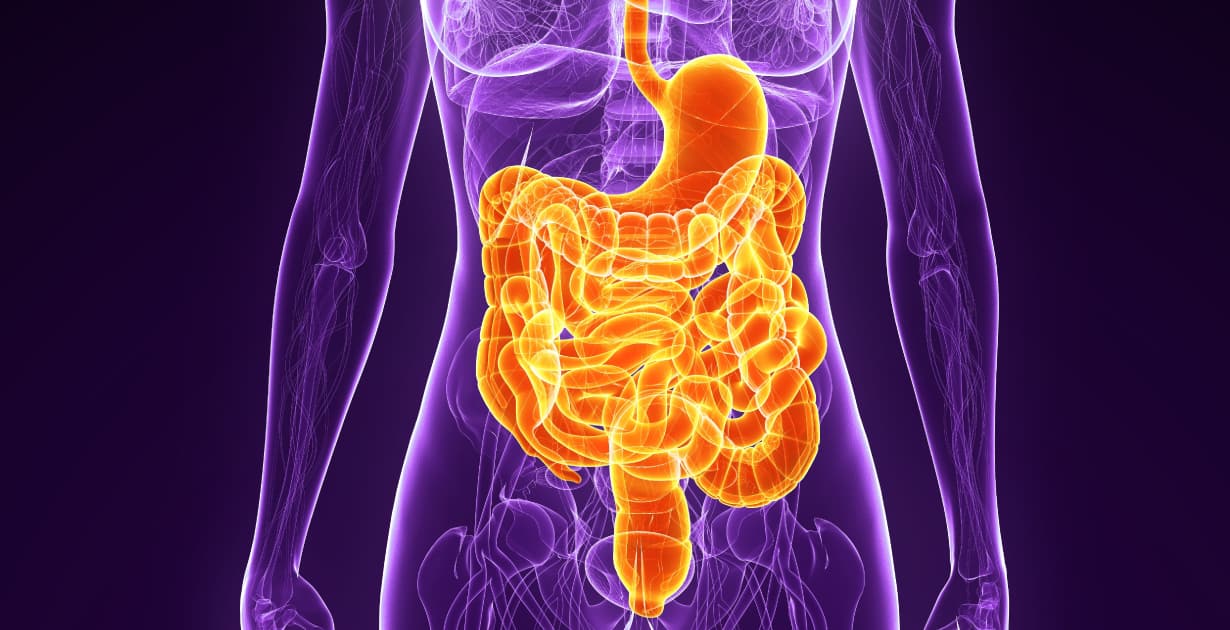
Small Intestine — The small intestine is where the majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients takes place. It is a long, coiled tube that is approximately 20 feet long and is divided into three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The small intestine receives chyme from the stomach and continues the digestion process by breaking down proteins, carbohydrates, and fats into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The walls of the small intestine are lined with tiny, finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for nutrient absorption.
Pancreas — The pancreas is a gland located behind the stomach that plays a vital role in digestion by producing digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which help neutralize stomach acid. The enzymes produced by the pancreas are released into the small intestine to further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into their basic building blocks.
Large Intestine (Colon) — The large intestine is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from the remaining indigestible food matter and forming it into solid waste, or stool. The colon is also home to billions of beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion and help maintain a healthy balance of gut flora. These bacteria play a crucial role in fermenting undigested carbohydrates, producing vitamins, and protecting against harmful pathogens.
Rectum and Anus — The rectum is the final section of the large intestine where stool is stored before being expelled from the body through the anus. The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive tract through which waste is eliminated.
Tips to Maintain a Healthy Digestive System
To keep your digestive system functioning optimally, it’s essential to follow some simple tips:
1. Eat a Healthy Diet — Include plenty of fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet to support healthy digestion and regular bowel movements. Avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive amounts of caffeine and alcohol.
2. Stay Hydrated — Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to help soften stool and prevent constipation. Herbal teas and coconut water can also be beneficial for hydration.
3. Exercise Regularly — Physical activity helps stimulate the muscles of the digestive tract and can prevent constipation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
4. Manage Stress — Chronic stress can negatively impact digestion and lead to symptoms like bloating, gas, and stomach pain. Practice stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
5. Get Plenty of Sleep — Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, including proper digestion. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support optimal digestive function.
6. Avoid Overeating — Eating large meals can put a strain on the digestive system and lead to indigestion. Try to eat smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day to support healthy digestion.
7. Listen to Your Body — Pay attention to how different foods make you feel and adjust your diet accordingly. If you notice symptoms like bloating, gas, or stomach pain after eating certain foods, consider eliminating them from your diet.
By following these tips and taking care of your digestive system, you can support overall health and well-being. Remember that the health of your digestive system is closely linked to your lifestyle choices, so making small changes can have a big impact on your digestive health.
Take the time to educate yourself about how your digestive system works and implement healthy habits to maintain optimal digestion. Your body will thank you for it!
The human digestive system is a complex network of organs that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. One crucial organ in this system is the liver, which plays a vital role in filtering and detoxifying the blood.
When we eat, the nutrients from our food are absorbed into the bloodstream and sent to the liver for processing. The liver has the remarkable ability to break down and store amino acids, synthesize and metabolize fats and cholesterol, store glucose, detoxify the blood, and regulate internal functions. It acts as a filter, removing toxins and waste products from the blood before they can harm the body.
Another important organ in the digestive system is the gallbladder. This small, pear-shaped organ stores and recycles excess bile from the liver, which is used for the digestion of fats. The gallbladder squeezes bile into the small intestine through bile ducts when we eat, helping to break down fats and aid in digestion.
The pancreas, a tube-shaped organ located near the liver and gallbladder, secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine to further break down food. It also produces insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. The pancreas plays a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, ensuring that the body receives the energy and building blocks it needs to function properly.
The small intestine, a long, thin tube that is about 20 feet long, is where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients takes place. The small intestine is lined with tiny protrusions called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. Enzymes on the villi break down nutrients into a form that can be easily absorbed by the body, while also helping to prevent leaky gut syndrome.
The colon, or large intestine, is the final stage of the digestive process. Waste products from the small intestine enter the colon, where water, vitamins, and minerals are absorbed. The colon is also home to beneficial bacteria that help with digestion and protect against harmful bacteria. Waste products are eventually eliminated from the body through the rectum in the form of stool.
In traditional Chinese medicine, the spleen is considered a crucial organ for the assimilation of nutrients and maintenance of physical strength. The spleen transforms digested food into usable nutrients and life energy force, known as qi. A breakdown in spleen function can lead to fatigue and weakness, affecting various organs in the body.
In both Western and Eastern medicine, the digestive system is recognized as a key component of overall health and well-being. Proper digestion and absorption of nutrients are essential for the body to function optimally and maintain good health. By understanding the roles of each organ in the digestive system and how they work together, we can better appreciate the importance of maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle to support digestive health. pylori bacteria, and stomach cancer
Conclusion
Our digestive system is a complex and intricate system that plays a crucial role in our overall health. The spleen, as a central organ in Traditional Chinese Medicine, is seen as essential for nourishing our bodies and promoting development.
By following the top 10 healthy tips to improve your digestive system, you can ensure that your digestive system functions efficiently and effectively. From chewing your food thoroughly to incorporating probiotics into your diet, there are many simple steps you can take to support your digestive health.
It’s important to listen to your body and pay attention to any signs of digestive system issues. If you experience symptoms like bloating, constipation, or abdominal pain, it may be a sign of a more serious digestive problem that requires medical attention.
Overall, taking care of your digestive system is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. By following these tips and being mindful of your digestive health, you can support your body’s natural healing abilities and promote optimal functioning of your digestive system.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a common bacterial infection that affects the digestive system. While many people with H. pylori infection may not experience any symptoms, the infection can lead to serious health complications, including an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Research has shown a strong association between H. pylori infection and the development of stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer. H. pylori is a major risk factor for stomach cancer, as the bacteria can cause chronic inflammation in the stomach lining, which can eventually lead to the growth of cancerous cells. In fact, H. pylori infection is considered a class 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization, meaning that it is a known cause of cancer in humans.
In addition to stomach cancer, H. pylori infection has also been linked to an increased risk of developing other types of cancer, including lymphoma of the stomach and esophageal cancer. The exact mechanisms by which H. pylori infection contributes to the development of these cancers are not fully understood, but it is believed that chronic inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive tract play a role.
It is important to note that not everyone with H. pylori infection will develop cancer. However, individuals with a family history of stomach cancer or other risk factors for cancer should be especially vigilant about getting tested and treated for H. pylori infection.
In addition to cancer, H. pylori infection can also lead to other digestive system disorders, including peptic ulcer disease and gastritis. Peptic ulcers are sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine, and they can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and indigestion. Gastritis is inflammation of the stomach lining, which can cause similar symptoms as peptic ulcers.
Treatment for H. pylori infection typically involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-reducing medications. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment to fully eradicate the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications.
In addition to medical treatment, making dietary and lifestyle changes can also help improve digestion and reduce the risk of complications from H. pylori infection. Eating a healthy diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and probiotic-rich foods can support digestive health and reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. Avoiding processed foods, alcohol, and tobacco can also help reduce the risk of complications from H. pylori infection.
Overall, H. pylori infection is a common bacterial infection that can lead to serious health complications, including an increased risk of cancer. By seeking treatment and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can reduce the risk of complications and support overall digestive health. If you have any concerns about H. pylori infection or its potential complications, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and treatment options. the topic of the benefits of practicing mindfulness in everyday life:
Mindfulness is a practice that has gained popularity in recent years for its numerous benefits on both mental and physical well-being. The concept of mindfulness is rooted in ancient Buddhist teachings, but has been adapted and incorporated into modern psychology and therapy techniques.
So, what exactly is mindfulness? Simply put, mindfulness is the practice of being present in the moment and paying attention to our thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. It involves being aware of our surroundings, our emotions, and our physical sensations without getting caught up in them.
One of the key benefits of practicing mindfulness is its ability to reduce stress and anxiety. By focusing on the present moment and letting go of worries about the past or future, mindfulness can help calm the mind and promote a sense of peace and relaxation. Research has shown that practicing mindfulness can lower levels of the stress hormone cortisol and reduce symptoms of anxiety disorders.
In addition to reducing stress, mindfulness has been shown to improve focus and concentration. By training our minds to be aware of the present moment, we can better focus on the task at hand and avoid distractions. This can be particularly helpful in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world where we are constantly bombarded with information and stimuli.
Furthermore, mindfulness can also improve our relationships with others. By being fully present and attentive in our interactions with others, we can better understand their perspectives, empathize with their emotions, and communicate more effectively. This can lead to stronger and more fulfilling relationships with friends, family, and colleagues.
Moreover, mindfulness has been linked to improved physical health. Studies have shown that practicing mindfulness can lower blood pressure, boost the immune system, and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses such as heart disease and diabetes. By reducing stress and promoting relaxation, mindfulness can have a positive impact on overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, incorporating mindfulness into our daily lives can have a myriad of benefits on our mental, emotional, and physical health. By being present in the moment, we can reduce stress, improve focus, enhance relationships, and promote overall well-being. So, why not give mindfulness a try and see the positive impact it can have on your life?